When the kneecap slips out of place — whether once or repeatedly — it’s more than a painful event. Patellar instability is a structural and biomechanical condition that can cause cartilage damage, recurrent injuries, and long-term joint degeneration if not evaluated with precision.
At SIGMA Orthopedics & Sports Medicine, our approach is different: We identify why the kneecap dislocates, assess every anatomic factor, and design a customized plan that restores stability while protecting your knee for life.
Patellar instability occurs when the kneecap slides out of the groove where it normally tracks. This may happen once during a traumatic injury—or become recurrent due to underlying anatomic issues such as trochlear dysplasia, patella alta, MPFL insufficiency, or rotational malalignment.
Traditional evaluations often miss the root cause of instability. The SIGMA Protocol uses a Six-Sigma, aviation-inspired diagnostic pathway that eliminates variance and identifies the exact biomechanical contributors that must be corrected.
High-definition imaging and AP/Lateral/Merchant views to assess:
MRI assessed through a patellar-specific lens:
If surgery is indicated, the SIGMA pathway identifies exactly which procedures (MPFL, tibial tubercle osteotomy, trochleoplasty, derotation osteotomy) will eliminate instability—not just “patch it.”
Seek evaluation if you experience:

Best for isolated, first-time traumatic events without major anatomic risk factors.
Includes:
Indicated when the ligament that stabilizes the kneecap is stretched, torn, or chronically insufficient.
SIGMA Reconstruction Advantages:
Used when structural abnormalities drive recurrent instability.
These may include:
Every surgical plan is fully customized based on SIGMA metrics—not a one-size-fits-all operation.
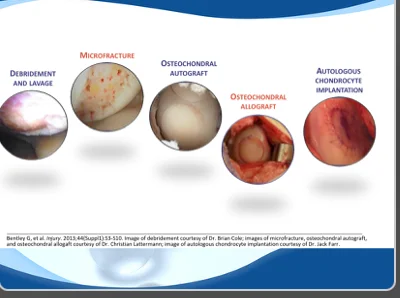
Recurrent instability injures cartilage every time the patella dislocates or subluxes.
SIGMA’s preservation strategy includes:
Goal: prevent early arthritis and safeguard long-term knee performance.
High-reliability rehabilitation designed for predictable, measurable outcomes.
Includes:
Each patient receives a precision recovery plan backed by Six Sigma metrics.

Common Symptoms: