A2M acts as a natural molecular “inhibitor shield,” blocking the destructive enzymes that damage cartilage in arthritis, tendon injuries, or post-traumatic joint degeneration.
Alpha-2 Macroglobulin (A2M) & Protease Inhibitor Therapy — a key pillar of the SIGMA SynerG™ Orthobiologics Suite
Alpha-2 Macroglobulin (A2M) is a naturally occurring protein in the blood that binds and neutralizes the enzymes responsible for cartilage breakdown — including the inflammatory molecules that accelerate arthritis and joint degeneration.
In simple terms:
✅ It stops the chemical process that destroys joints
✅ It slows the progression of arthritis at the cellular level
✅ It protects the cartilage you still have
This is not a steroid, viscosupplement, or pain-numbing injection. It’s a biologic treatment that targets the root cause of tissue breakdown.
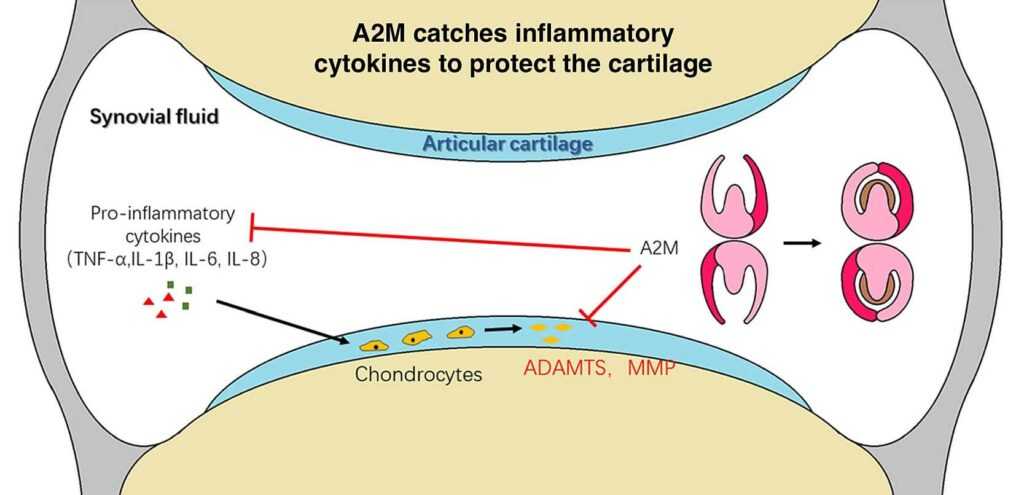
Once injected into the affected joint, A2M:
🛡️ Blocks inflammatory breakdown enzymes
🧬 Protects cartilage from further degeneration
🔄 Creates a biologic environment favorable for healing
⏳ May delay or prevent the need for joint replacement


✅ Early to moderate osteoarthritis (knee, hip, shoulder, ankle)
✅ Post-traumatic cartilage injury (after ACL tear, meniscus tear, etc.)
✅ Failed steroid, HA, or PRP injections
✅ Chronic tendinopathy or ligament breakdown
✅ Active adults or athletes trying to avoid joint replacement
✅ Personal injury patients with documented joint damage
Callout Quote:
“We don’t just inject biologics — we engineer the right treatment plan for the right patient at the right time.”
— Dr. Frank McCormick, MD
Standard Clinics | SIGMA Method |
Single, untracked injection | Protocol-based treatment plan (1–3 stage approach) |
No imaging to confirm placement | Ultrasound + fluoroscopic precision delivery |
No follow-up outcome measurement | PRO-tracked recovery in SIGMA Scoreboard |
Trial-and-error based | Evidence-based + patient-specific biologic dosing |
No surgical context | Direct decision-tree: biologics → surgery if needed |
Not in every case — but it may delay or prevent surgery for the right patient and slow degeneration until surgery is truly needed.
No — this treatment is most effective before full cartilage loss, not after.
Not yet. However, we offer flexible payment options and medical-legal documentation for personal injury and workers’ comp cases.
Many patients experience sustained benefit for 6–24+ months depending on joint damage, activity level, and overall health.
No. PRP and BMAC stimulate healing. A2M protects the joint from further damage. They are often used together in our SynerG biologic protocols.
In the field of orthopedic sports medicine, the search for innovative treatments to enhance recovery and improve outcomes continues to evolve. Alpha-2 macroglobulin (A2M) and protease inhibitors have emerged as promising therapeutic agents, offering potential benefits in managing various musculoskeletal conditions. This report examines the clinical efficacy and applications of these substances in orthopedic sports medicine.
A2M, a large plasma protein, acts as a broad-spectrum protease inhibitor. It binds and inactivates proteases, including matrix metalloproteinases and inflammatory cytokines, helping maintain a balance between tissue breakdown and repair. Clinical applications of A2M are being investigated in several areas. For osteoarthritis, intra-articular A2M injections have shown promise in reducing pain and improving function. In tendinopathies, particularly chronic cases resistant to conventional treatments, A2M injections may reduce inflammation and promote tissue healing. For ligament and muscle injuries, A2M’s anti-inflammatory properties could potentially accelerate healing and return to play for athletes.
Protease inhibitors, including matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors, serine protease inhibitors, and cysteine protease inhibitors, are also being studied for their potential benefits. These agents target specific enzymes involved in tissue degradation, potentially preserving cartilage and other connective tissues. Their applications are being explored in osteoarthritis, tendon and ligament injuries, post-surgical recovery, and muscle injuries. While early clinical evidence for both A2M and protease inhibitors is encouraging, larger, randomized controlled trials are needed to establish definitive efficacy. Researchers are also investigating combination therapies, exploring potential synergistic effects of A2M and specific protease inhibitors in managing complex orthopedic conditions.
Mechanism of Action:
– A2M is a large plasma protein that acts as a broad-spectrum protease inhibitor
– Binds and inactivates proteases, including matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and inflammatory cytokines
– Helps maintain balance between tissue breakdown and repair
Clinical Applications:
1. Osteoarthritis (OA):
– Intra-articular A2M injections show promise in reducing pain and improving function
– May slow cartilage degradation by inhibiting catabolic enzymes
2. Tendinopathies:
– A2M injections potentially reduce inflammation and promote tissue healing
– Particularly beneficial in chronic cases resistant to conventional treatments
3. Ligament Injuries:
– A2M may enhance ligament healing by modulating the inflammatory response
– Potential applications in accelerating return to play for athletes
4. Muscle Injuries:
– A2M’s anti-inflammatory properties may aid in reducing muscle damage and enhancing recovery
Clinical Evidence:
– Several small-scale studies demonstrate positive outcomes in OA patients
– Limited but encouraging data for tendinopathies and ligament injuries
– Larger, randomized controlled trials needed to establish definitive efficacy
Types and Mechanisms:
1. Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors (MMPIs):
– Target specific MMPs involved in tissue degradation
– May help preserve cartilage and other connective tissues
2. Serine Protease Inhibitors:
– Inhibit enzymes like elastase and cathepsin G
– Potential to reduce inflammation and tissue damage
3. Cysteine Protease Inhibitors:
– Target enzymes such as cathepsins
– May play a role in preventing bone and cartilage degradation
Clinical Applications:
1. Osteoarthritis:
– MMPIs show potential in slowing cartilage degradation
– Combination therapies with other agents being explored
2. Tendon and Ligament Injuries:
– Protease inhibitors may help maintain tissue integrity during healing
– Potential to reduce scarring and improve functional outcomes
3. Post-surgical Recovery:
– Application of protease inhibitors during or after surgery may enhance healing and reduce complications
4. Muscle Injuries:
– Inhibition of proteases involved in muscle breakdown may accelerate recovery
Clinical Evidence:
– Preclinical studies show promising results in various musculoskeletal conditions
– Limited clinical trials available, with mixed results
– Further research needed to optimize dosing, delivery methods, and specific indications
Combination Therapies:
– Synergistic effects of A2M and specific protease inhibitors being investigated
– Potential for enhanced efficacy in managing complex orthopedic conditions
Challenges and Considerations:
1. Delivery Methods:
– Optimizing local delivery to target tissues
– Exploring sustained-release formulations for prolonged effects
2. Dosing:
– Determining optimal concentrations for different conditions
– Balancing efficacy with potential side effects
3. Patient Selection:
– Identifying subgroups most likely to benefit from these therapies
– Considering individual factors such as age, activity level, and comorbidities
4. Cost-effectiveness:
– Evaluating the economic impact of these treatments compared to conventional therapies
5. Long-term Effects:
– Assessing the safety and efficacy of repeated treatments
– Monitoring for potential systemic effects
Alpha-2 macroglobulin and protease inhibitors represent a promising frontier in orthopedic sports medicine. While early clinical evidence suggests potential benefits in managing various musculoskeletal conditions, further research is needed to fully elucidate their efficacy, optimal use, and long-term outcomes. As our understanding of these agents grows, they may become valuable tools in the orthopedic surgeon’s arsenal, offering new options for enhancing tissue repair, reducing inflammation, and improving patient outcomes. The integration of these therapies into clinical practice will require careful consideration of patient factors, treatment protocols, and cost-effectiveness. Continued research and clinical trials will be essential in determining the true potential of A2M and protease inhibitors in revolutionizing the management of orthopedic sports injuries and degenerative conditions.